What is Diaphoresis?
Diaphoresis is a medical condition characterized by abnormal, excessive sweating. Unlike the typical sweating that occurs due to heat or physical activity, diaphoresis happens independently and often without an obvious trigger. The skin may appear pale or white, and feel clammy. Understanding diaphoresis involves recognizing its causes, identifying its symptoms, and learning how to effectively manage it. It’s important to distinguish diaphoresis from other conditions to ensure the correct diagnosis and treatment. This guide will delve into the essential aspects of diaphoresis, providing you with valuable information to help you understand and manage this condition.
The Difference Between Diaphoresis and Other Skin Conditions
Diaphoresis often presents with symptoms that can be similar to other skin conditions, but there are key differences. The pale, clammy skin associated with diaphoresis is a critical distinguishing factor. Conditions like eczema or psoriasis primarily involve inflammation, redness, and scaling of the skin, but they don’t typically present with excessive sweating or the specific skin appearance of diaphoresis. Other conditions like heat rash can cause skin irritation and redness, which differs from the whitening and clamminess linked to diaphoresis. By focusing on the combination of excessive sweating and the unique skin characteristics, you can often differentiate diaphoresis from other skin conditions.
Symptoms to Watch For

Identifying the symptoms of diaphoresis is crucial for early detection and effective management. The primary symptoms include excessive sweating, skin whitening, and clammy skin. Each symptom provides important clues about the condition. Recognizing these symptoms can help individuals seek medical attention promptly and receive the appropriate diagnosis and treatment. The combination of these symptoms, rather than a single symptom, is a significant indicator of diaphoresis, enabling healthcare professionals to differentiate it from other medical issues that might mimic some of its signs.
Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating is the most noticeable symptom of diaphoresis. It is characterized by profuse perspiration that occurs independently of external factors such as heat or physical exertion. This can lead to significant discomfort and disruption in daily activities. This sweating may affect the whole body or be localized to specific areas such as the palms, soles, or armpits. Monitoring the frequency, duration, and intensity of the sweating episodes is crucial for medical evaluation and determining the underlying cause of the condition. The amount of sweat produced often surpasses what is normal for the individual, indicating a potential health concern.
Skin Whitening
Skin whitening, or pallor, is another key symptom of diaphoresis. It occurs when the skin becomes pale or white due to reduced blood flow to the surface. This is often linked to the body’s response to stress or certain underlying medical conditions. The whitening can be particularly noticeable in areas where the skin is thinner, such as the face or hands. Observing changes in skin color, in conjunction with excessive sweating, can provide vital clues to understanding the presence of diaphoresis. Recognizing this symptom can help facilitate a prompt and accurate diagnosis, crucial for appropriate medical intervention.
Clammy Skin
Clammy skin is a texture often associated with diaphoresis. The skin feels cold and moist, caused by sweat collecting on the surface. This sensation is a result of the body’s attempt to regulate its temperature, and it often accompanies other symptoms like excessive sweating and skin whitening. This characteristic can be an important indicator of a health condition. Experiencing clammy skin can be uncomfortable and may point to other underlying medical conditions. This combination of symptoms warrants seeking medical advice to determine the cause and begin appropriate treatment.
Possible Causes of Diaphoresis
Diaphoresis can arise from various factors, often linked to underlying medical conditions, medications, or environmental influences. Identifying the cause is a vital part of managing the condition effectively. Possible triggers range from serious health issues to specific drugs or external settings. Understanding the potential causes allows healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and recommend appropriate treatments to alleviate the symptoms and address the root problem. This comprehensive investigation aids in customizing the healthcare approach to each individual’s unique circumstances.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Several underlying medical conditions can trigger diaphoresis. These can vary from heart conditions to infections, which all impact the body’s ability to regulate temperature and blood flow. For example, a heart attack can cause diaphoresis as the body attempts to cope with the stress on the cardiovascular system. Additionally, infections such as sepsis can lead to significant sweating and changes in skin appearance. Early identification of the underlying medical cause is essential for effective treatment and managing the associated symptoms. Comprehensive diagnostics are crucial to rule out or diagnose these conditions and offer the necessary care.
Medications and Their Effects
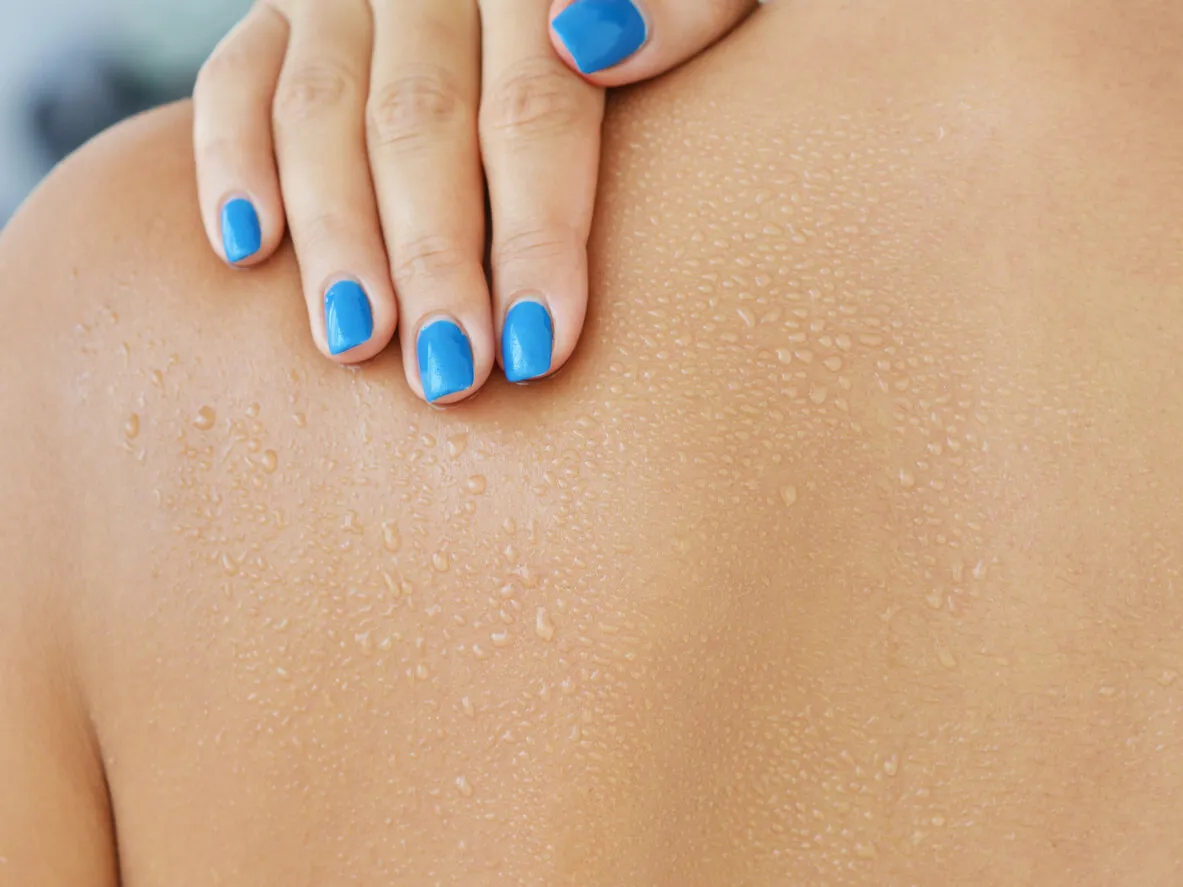

Certain medications can lead to diaphoresis as a side effect. These include a range of drugs, from antidepressants to medications used for diabetes. These drugs may interfere with the body’s temperature regulation mechanisms or affect the autonomic nervous system, which controls sweating. Recognizing the potential link between medication use and diaphoresis is vital to manage the condition effectively. If a patient experiences excessive sweating after starting a new medication, it is important to consult a doctor to discuss adjustments to the treatment plan or explore alternative medications that do not cause these side effects.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also play a role in triggering diaphoresis. Exposure to extreme temperatures or high humidity can increase the likelihood of excessive sweating, even in healthy individuals. The body attempts to cool itself through sweating when exposed to heat, but sometimes the response becomes overactive, leading to diaphoresis. Understanding the impact of these environmental influences allows individuals to take precautions to reduce sweating episodes, such as staying in cool environments or wearing breathable clothing. Adjusting to external conditions is a common strategy, particularly for those prone to diaphoresis, helping manage the symptoms.
Top 7 Facts About Diaphoresis
Fact 1 Overview
Diaphoresis is characterized by excessive, often unexplained sweating and changes in skin appearance, such as whitening and feeling clammy. It is a symptom, not a disease in itself, and usually indicates an underlying medical condition or external factors. The primary concern is the cause, which could range from benign issues to life-threatening emergencies. The primary focus involves diagnosing the root cause by understanding a range of factors, including medical history, current medications, and environmental conditions.
Fact 2 The Physiology
The physiology of diaphoresis involves the autonomic nervous system, responsible for controlling bodily functions, including sweating. When the body experiences stress, infection, or changes in temperature, the sympathetic nervous system activates sweat glands. In diaphoresis, this response is often overstimulated, causing excessive sweating. The body’s attempt to regulate its temperature through this process can cause significant discomfort and disruption in normal activities, often accompanied by changes in skin color and texture.
Fact 3 Causes and Triggers
The causes of diaphoresis range from various medical conditions to environmental factors. Heart-related issues, infections, and certain medications can all trigger it. External factors, like extreme heat or humidity, may also cause the condition. Knowing the possible causes allows for targeted assessments and the implementation of measures to manage the condition effectively. Identifying the particular trigger enables a patient to mitigate the symptoms and improve overall health.
Fact 4 Risk Factors
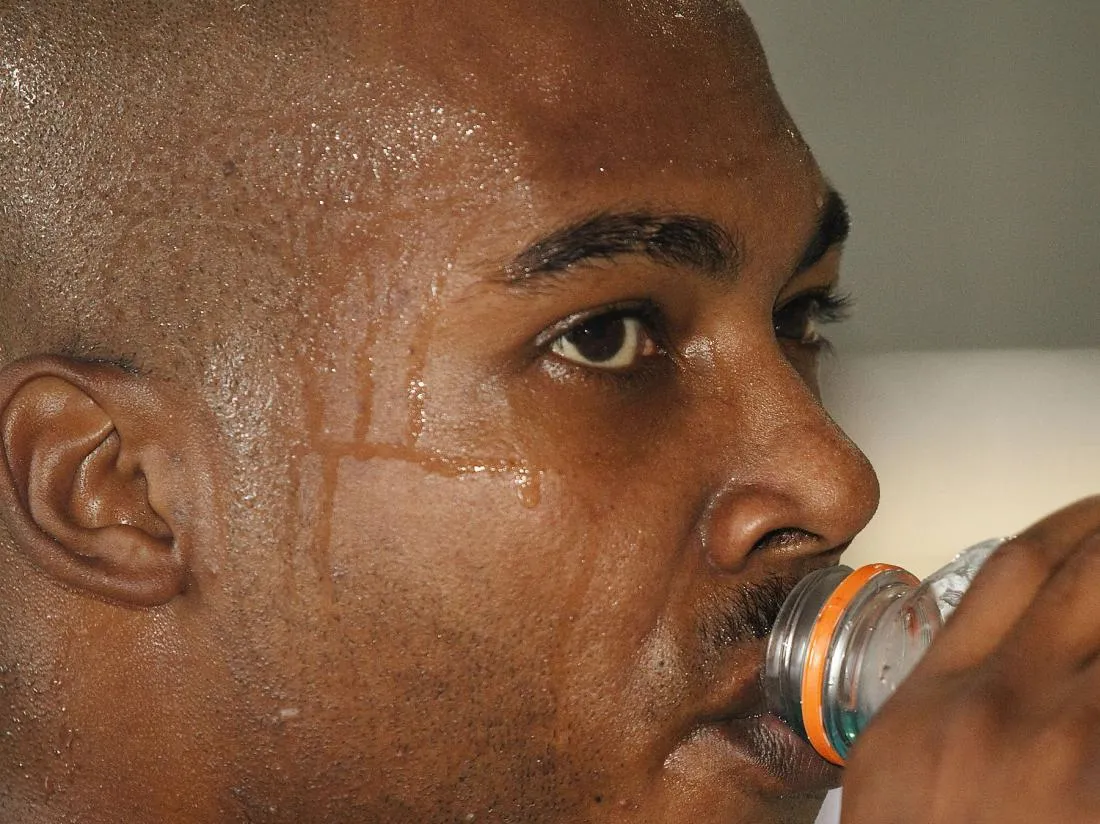

Several factors can raise the risk of experiencing diaphoresis. Those with pre-existing medical conditions such as heart disease or diabetes may be more susceptible. Moreover, anyone taking certain medications that impact the nervous system or hormone balance may be at increased risk. Lifestyle choices like alcohol consumption or nicotine use can also contribute to the likelihood of developing diaphoresis. Comprehensive risk assessment will help healthcare providers customize healthcare strategies to manage the condition.
Fact 5 Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process for diaphoresis usually begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers evaluate symptoms, medical history, medications, and lifestyle factors. Diagnostic tests might include blood tests, ECGs, or imaging scans to identify underlying causes, such as heart issues or infections. Accurately identifying and treating the root causes will lead to improved symptom management and enhance a patient’s overall health and well-being.
Fact 6 The Treatment Options
Treatment options for diaphoresis vary based on the underlying cause and severity. If an underlying medical condition triggers diaphoresis, addressing that condition is the primary goal. Treatments include medications, such as anticholinergics to reduce sweating, or lifestyle changes, such as adjusting the diet or changing medications. Additional interventions may include wearing moisture-wicking clothing and managing environments to keep them cool. The treatment plan is personalized for each patient.
Fact 7 Prevention and Management
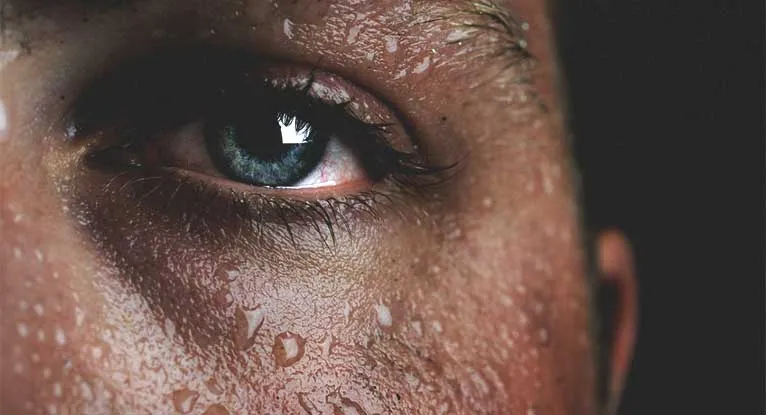

Preventative measures and ongoing management are crucial for those with diaphoresis. This includes lifestyle adjustments like staying hydrated, avoiding triggers such as alcohol and spicy foods, and wearing breathable clothing. Regular medical check-ups can help monitor conditions and assess any new symptoms that might indicate the need for a treatment change. Individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of diaphoresis by adopting these preventative measures.
How to Manage Diaphoresis
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle adjustments can play a key role in managing diaphoresis and reducing the frequency and intensity of sweating episodes. This involves making small changes to your daily routine that have significant impact on your comfort level. Such as wearing loose, breathable clothing that allows the skin to breathe freely and reduces heat retention. Another is maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine, that may stimulate the nervous system and increase sweating. Staying well-hydrated is also important, as dehydration can exacerbate symptoms.
Medical Treatments
Several medical treatments are available to manage diaphoresis when lifestyle adjustments are not enough. Antiperspirants are useful as they block the sweat ducts and reduce sweating, particularly in the armpits. In some cases, medications such as anticholinergics may be prescribed to decrease nerve stimulation, helping reduce the overall sweating. For more severe cases, medical procedures may be suggested, such as iontophoresis, which uses electrical currents to reduce sweating in the palms and soles, or in rare cases, surgery to remove or damage the sweat glands. The choice of treatment depends on the specific cause and severity of the diaphoresis.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to seek medical attention for diaphoresis is crucial. If you experience frequent or excessive sweating with no obvious triggers, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. It’s particularly important to seek medical help if diaphoresis is accompanied by other symptoms, such as chest pain, dizziness, or difficulty breathing. These symptoms could be signs of an underlying medical condition that requires immediate medical intervention. A proper diagnosis can lead to appropriate management and prevent potential complications.
In conclusion, diaphoresis is a complex condition that demands a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. From understanding the difference between diaphoresis and other conditions to recognizing the top facts and implementing lifestyle changes, the information here aims to equip you with the tools and knowledge to manage this condition effectively. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.